
Is the Future of Industrial Automation on the Edge?
Edge computing is rapidly emerging as the cornerstone of industrial automation, transforming sectors with cutting-edge technologies like IoT, AI/ML, and 5G connectivity. By enabling data processing closer to its source, edge computing enhances real-time decision-making, operational resilience, and connectivity in industrial environments. This shift is reshaping industries, driving efficiency, productivity, and cost savings, with significant implications for global economic growth and sustainability goals.
![[object Object]](https://admin.industrialautomationindia.in/storage/articles/article-paxJf0WcRlMO3PPMnbk5bZn4mGqJhHJIEJLb4dOC.jpg)
Edge computing is rapidly becoming the cornerstone of industrial automation, says Bhavesh Goswami, Founder & CEO, CloudThat.
Industrial automation is undergoing a seismic transformation powered by cutting-edge technologies like edge computing, cloud computing, the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML), and 5G connectivity. Among these, edge computing is emerging as the linchpin, enabling industries to process data closer to its source for faster decision-making, enhanced autonomy, and operational resilience.
This shift is reshaping industries by driving operational efficiency, enhancing productivity, and reducing costs. For economies like India, adopting these advancements could prove pivotal in achieving ambitious goals, such as becoming a $5 trillion economy by 2025.
This article explores how edge computing, in conjunction with other transformative technologies, is enabling smarter, more connected industrial systems and revolutionising the automation landscape.
Edge Computing: The Key to Industrial Transformation
Unlike traditional cloud computing, which relies on centralised data centers, edge computing processes data locally, closer to the devices generating it. This significantly reduces latency, enhances real-time decision-making, and ensures system reliability even when connectivity to the cloud is disrupted.
Real-World Use Case: Siemens’ Edge-Enabled Automation
Siemens Energy has integrated edge computing with IoT to connect autonomous vehicles, robots, and CNC machines. By processing data at the edge, Siemens has achieved real-time energy monitoring, a 50% reduction in manual data collection time, and a 25% decrease in maintenance costs. These advancements align with Siemens' goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2030, showcasing how edge computing can address both operational and sustainability goals.
Benefits of Edge Computing in Industrial Automation
- Real-Time Processing: Reduces latency for critical applications like predictive maintenance, quality control, and anomaly detection.
- Enhanced Reliability: Systems can operate independently during cloud outages.
- Cost Efficiency: By minimising data transmission to the cloud, industries save significantly on bandwidth and storage costs.
How Edge Computing Integrates with Other Technologies
1. Edge + IoT: Enabling Smarter Industries
IoT and edge computing together create a connected ecosystem where devices collect, process, and analyse data in real-time. This minimises delays, maximises actionable insights, and ensures seamless operations even in remote areas.
Use Case: Caterpillar’s Predictive Maintenance
Caterpillar has deployed IoT sensors integrated with edge computing to predict equipment failures. This has saved millions in unplanned downtime, enabling the company to deliver insights on-site without depending on cloud-based systems.
Energy Efficiency
IoT devices at the edge can monitor and optimise energy consumption, supporting sustainability initiatives. For instance, edge-enabled IoT systems can dynamically adjust lighting or HVAC systems in factories to save energy.
2. Edge + AI/ML: Real-Time Intelligence
Combining edge computing with AI/ML capabilities unlocks new possibilities for industrial automation. AI/ML algorithms deployed on edge devices can detect anomalies, perform predictive analytics, and automate decision-making—all in real-time.
Use Case: Rolls-Royce’s Borescope Analysis
Rolls-Royce uses AI-powered borescopes at the edge to inspect aircraft engines. This has reduced inspection times by 75% and saved clients approximately £100 million over five years.
Key Benefits
- Quality Assurance: Faster anomaly detection leads to improved production quality.
- Autonomous Operations: Intelligent systems reduce dependency on human intervention, enhancing overall productivity.
3. Edge + 5G: Accelerating Industrial Connectivity
The low-latency, high-bandwidth capabilities of 5G make it an ideal enabler for edge computing in industrial environments. Together, they ensure seamless communication between edge devices and centralised systems, fostering real-time control and monitoring.
Use Case: Ericsson’s Smart Factory
Ericsson's Texas-based smart factory leverages 5G and edge computing to transform operations. By utilising autonomous guided vehicles and collaborative robots, the factory exemplifies the potential of 5G-enabled edge solutions. As part of its sustainability commitment, Ericsson aims to achieve carbon neutrality across its operations by 2030, with the smart factory already operating 24% more energy-efficiently than baseline metrics.
5G is expected to create $13.1 trillion in global economic value by 2035, with manufacturing contributing a significant portion, according to Qualcomm.
Enhanced Connectivity
5G ensures that edge devices remain synchronised with central systems, even for data-intensive applications like video analytics and augmented reality maintenance tools.
India’s Edge in Automation
For a rapidly growing economy like India, embracing edge computing is critical to modernising industries and driving economic growth. The NASSCOM AI Adoption Index estimates that data and AI could contribute $450-$500 billion to India’s GDP by 2025, with edge computing playing a significant role in this transformation.
Real-World Example: L&T’s Smart City Solutions
The integration of IoT and edge computing by Larsen & Toubro (L&T) for smart urban infrastructure in Nagpur, including the implementation of a smart lighting system that improves energy efficiency, has been part of the city's transformation into a large-scale integrated smart city. This initiative involves deploying advanced technologies like smart ICT systems for lighting, transport, and waste management.
Advantages for India
- Cost Reduction: Edge computing minimises operational expenses, especially in resource-intensive sectors like agriculture and logistics.
- Skilled Workforce: Accelerates the demand for high-tech roles, fostering innovation.
- Sustainability: Promotes energy-efficient and environmentally conscious systems aligned with India’s green initiatives.
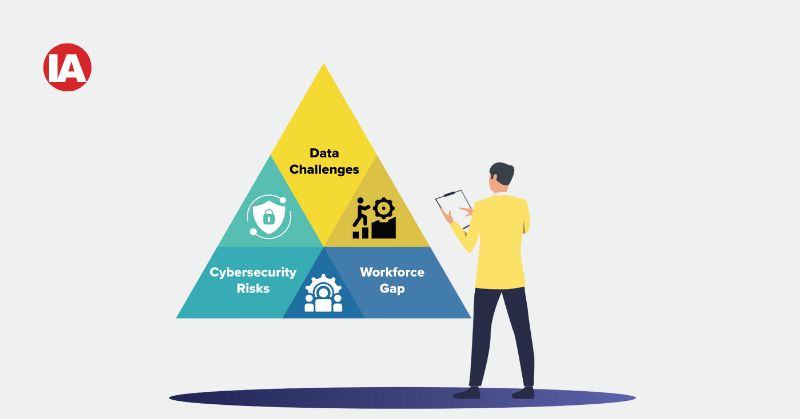
Challenges and Opportunities
Challenges
- Data Challenges Persist: Establishing edge infrastructure involves significant upfront costs. In a separate survey, nearly 70% of manufacturers identified data-related issues—such as quality, contextualisation, and validation—as the primary barriers to successful AI implementation.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased connectivity at the edge necessitates robust data protection measures to safeguard sensitive information.
- Workforce Gap: The demand for skilled professionals in edge computing and AI/ML outpaces supply.
Opportunities
- Global Competitiveness: Edge-enabled automation can boost productivity making industries more competitive on a global scale.
- Economic Growth: Investments in edge solutions unlock new revenue streams and reduce inefficiencies.
- Sustainability Gains: Edge computing reduces energy consumption and carbon footprints, aligning with global environmental goals.
Future Trends in Edge Computing for Industrial Automation
1. AI-Driven Edge Robotics
Intelligent robots equipped with edge computing capabilities will revolutionise manufacturing, enabling greater autonomy and efficiency. For example, Amazon’s robotic systems have reduced warehouse packaging times by 70%.
2. Edge-First Data Processing
Gartner predicts that by 2025, 75% of industrial data will be processed at the edge, driving faster decision-making and reducing dependency on centralised systems.
3. Sustainable Automation
Edge computing will prioritise green solutions, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and promoting energy-efficient operations.

Conclusion
Edge computing is rapidly becoming the cornerstone of industrial automation, driving innovation, sustainability, and efficiency across sectors. By processing data locally, it empowers industries to make real-time decisions, reduce costs, and ensure system reliability.
When combined with complementary technologies like IoT, AI/ML, and 5G, edge computing creates a future-ready ecosystem capable of tackling the challenges of Industry 4.0. For countries like India, investing in edge technologies is not just a necessity but a strategic imperative to achieve economic aspirations and compete globally.
By fostering research and development, implementing supportive policies, and upskilling the workforce, India can unlock the full potential of industrial automation on the edge. As edge computing evolves, it promises to redefine industries, merging efficiency, intelligence, and sustainability to deliver unprecedented opportunities for growth and innovation.
Bhavesh Goswami loves working with cutting edge technologies and creating products and services leveraging them. In a career spanning over 22 years, he has been working in the Cloud Computing space for about 18 years starting with the dev team of Amazon Web Services S3 team (2005) and later at Microsoft for their Big Data platform called Cosmos.
Bhavesh currently runs CloudThat, a Cloud, DevOps, AL/ML and security training & consulting company, with offices in India, USA, UK and Bangladesh. He is also co-founder at CloudAttack where he is striving to revolutionise the way people learn cloud.
______________________________________________________________________________________________
For a deeper dive into the dynamic world of Industrial Automation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA), explore our comprehensive collection of articles and news covering cutting-edge technologies, robotics, PLC programming, SCADA systems, and the latest advancements in the Industrial Automation realm. Uncover valuable insights and stay abreast of industry trends by delving into the rest of our articles on Industrial Automation and RPA at www.industrialautomationindia.in