
Motion Control, Smart Conveyance and Machine-Integrated Robots
Samantha Mou explores the evolving opportunities in motion control driven by advancements in smart conveyance systems and machine-integrated robots. These innovative technologies are set to transform the industrial automation landscape despite the ongoing challenges in the global machinery market.
![[object Object]](https://admin.industrialautomationindia.in/storage/articles/article-bfh3TAw72tTT3GEauzgSAlERCe4ElM6emtA5gTov.jpg)
Samantha Mou examines new opportunities for motion control in rapidly expanding smart conveyance and machine-integrated robot markets.
Due to high interest rates, elevated inventory and sluggish demand, the global machinery industry has been facing a tough year in 2024. This has been affecting sales of industrial automation components to machine builders (OEMs), including motion control products. Despite this, innovative technologies continue to create new opportunities for motion control, attracting new entrants to the market through product launches or partnerships. In this insight, we will discuss two new growth areas identified from our research and conversations with manufacturers: smart conveyance technology and robots with machine-integrated control.
Smart conveyance technology
Smart conveyance technology is a multi-carrier transport technology and is available as either linear or planar systems. The market for linear systems has surged over the past three years, with sales revenue growing from $237 million in 2020 to $488 million in 2023. By 2029, sales of linear systems are expected to exceed $1.1 billion, nearly five times the market size in 2020. Planar technology is still in its trial period, generating sales of nearly $20 million in 2023.
Since Interact Analysis began tracking smart conveyance market data in 2020, the food, pharmaceutical and general packaging industries were the main application markets for smart conveyance systems until 2022. However, over the past 2-3 years, the landscape has changed with the rapid penetration of smart conveyance products in the Asian market, and a sharp increase in sales from the battery and electronics industries.
Encouraged by the growth momentum, new entrants are rapidly entering the market. As shown in the chart below, the number of suppliers almost doubled in 2023 compared with the year before. As of October, 12 more companies have launched new linear smart conveyance products in 2024. Most recently, German rotary indexer and conveyor manufacturer TAKTOMAT presented its new linear smart conveyor system powered by SEW Eurodrive at the Motek trade show. TAKTOMAT’s key clients are primarily from the automotive sector, so the new product is expected to have applications within this industry.
Although new vendors have not acquired meaningful market share, as the supplier base has not yet consolidated, we expect they will increase their presence, especially in their local markets; China, Japan and Europe.
Beyond this, Interact Analysis has also conducted research with companies planning to launch new smart conveyance technology products within the next few years. Most of them are suppliers of motion control components such as linear motors and servo products, or conveyor manufacturers. After the cyclical downturn in the machinery industry comes to an end, we expect the revenue and supplier base of smart conveyance systems to see promising growth in Europe and North America, driven by developments in battery manufacturing and warehouse automation.
Naturally, rising demand for smart conveyance technology represents a growing market for motion control products, including servo and direct drive technologies. Rather than offering smart conveyance systems in their own portfolio, some vendors are supplying key components to system providers. For example, many automation companies, including Rockwell and Siemens, have partnerships with Planar Motor Inc. (PMI), which makes planar smart conveyance products, to equip PMI systems with servo drives and controllers.
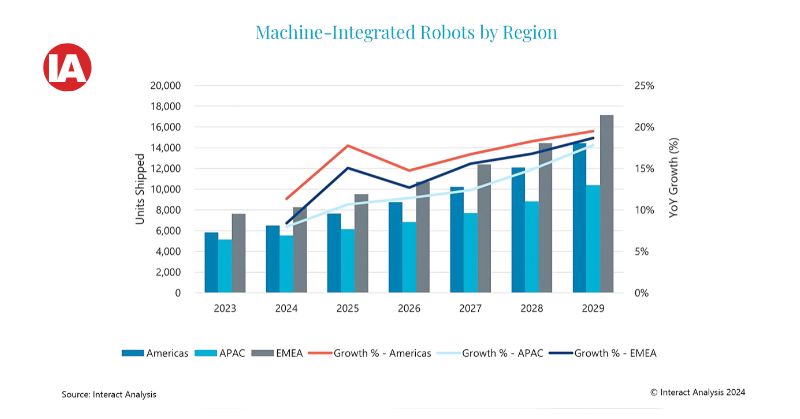
Machine-integrated robots

The term machine-integrated robots refers to robots that are fully integrated into machine control platforms, either by eliminating robot-specific controllers or by retaining robot controllers but integrating the programming platform into the machine systems. The first approach is more common for those machine-integrated robots currently deployed, which include customised robots made by machine builders (OEM-manufactured robots).
In 2023, global machine-integrated robot shipments reached nearly 20,000 units, of which shipments in the Americas, EMEA and Asia-Pacific regions accounted for 31%, 41% and 28% respectively. From 2023 to 2029, the market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.6%. Compared with the standard industrial robot market (with annual shipments of more than 520,000 units), the machine-integrated robot market is currently much smaller but is expected to grow at a faster rate.
The shortage of experienced engineers is one of the major drivers of growth for the machine-integrated robot market. By integrating robot and machine controllers, engineers can control machines and robots in a unified development environment, without using robot programming languages. This helps reduce challenges for both machine builders and end users in finding or training engineers and operators for robotic machines.
OEMs’ motivations to build robots in-house are also fueling the adoption of machine-integrated robots. Machine builders and integrators increasingly have the capability to build mechanical parts for robots, with some OEMs choosing to make robots by themselves to save costs. In customised scenarios, OEMs build special robot kinematics in-house, with a general automation controller enabling the practical integration of OEM-made robots with machines.
New entrants and partnerships are increasing the number of solutions available for machine-integrated robots. Robot manufacturers, machine builders and motion control system suppliers are all actively introducing new products and solutions.
For example, Rockwell Automation partnered with autonox Robotics in 2023, having previously entered a partnership with Atom Robot in late 2022. Now, robot arms from three robot vendors can be directly equipped with Rockwell PLCs. Most recently, Siemens confirmed new cooperation agreements with collaborative robot makers Universal Robots and Jaka, further expanding the range of robots that can be directly programmed on its platform. In the meantime, motion control suppliers also work closely with machine builders to provide solutions for OEM-made robots. For example, SEW offers a “Parallel Arm Kinematics Kit” to OEMs looking to make their own delta robots. In China, many packaging machinery manufacturers exhibited machines with picking robots made in-house at the recent CIIF tradeshow.
Final thoughts
The surging smart conveyance market and the emergence of machine-integrated robots offer new opportunities to motion control suppliers. Driven by the trends of digitalisation, flexibility, and ease-of-use in the manufacturing industry, both technologies are expected to increase their penetration in the machinery industry. Despite current challenges, many suppliers are preparing strategies for the next growth cycle. Companies with competitive products and solutions will gain an advantage when demand inevitably picks up.
Samantha Mou, a Research Analyst based in China, provides support in the Industrial Automation sector. Samantha brings with her a master’s degree in Economics, and has experience, whilst working in Germany, conducting market research in Industrial Equipment and Automobile Components.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________
For a deeper dive into the dynamic world of Industrial Automation and Robotic Process Automation (RPA), explore our comprehensive collection of articles and news covering cutting-edge technologies, robotics, PLC programming, SCADA systems, and the latest advancements in the Industrial Automation realm. Uncover valuable insights and stay abreast of industry trends by delving into the rest of our articles on Industrial Automation and RPA at www.industrialautomationindia.in